သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်း
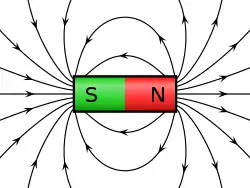
သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်း သည် လျှပ်စီးကြောင်းနှင့် သံလိုက်ထည်များ၏ သံလိုက်အကျိုးသက်ရောက်မှုဟု ဆိုနိုင်သည်။ သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းများကို အခြေခံကျသော ကွမ်တမ် ဂုဏ်အင်၊ ယင်းတို့၏ စပင်များနှင့် ဆက်နွယ်သည့် အခြေခံအမှုန်၏အရွေ့နှင့် ရွေ့လျားနေသော လျှပ်စစ်ဓာတ်တို့ဖြင့် ထုတ်လုပ်နိုင်သည်။[1][2] အထူးနှိုင်းရသီအိုရီအရ လျှပ်စစ်နှင့် သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းတို့သည် electromagnetic tensor ဟုခေါ်သည့် အကြောင်းအရာတစ်ခုတည်း၌ အပြန်အလှန် ဆက်နွယ်ကြသည်။ ကွမ်တမ် ရူပဗေဒ၌မူ လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းသည် ကွမ်တမ်ပြုခံရပြီး လျှပ်စစ်သံလိုက် အပြန်အလှန်ဆက်နွယ်မှုများသည် ဖိုတွန်များ ဖလှယ်ရာမှ ဖြစ်ပေါ်လာသည်။ သံလိက်စက်ကွင်းများသည် ယနေ့ခေတ်တွင် တွင်ကျယ်စွာ အသုံးပြုနေကြသည်။ လျှပ်စစ် အင်ဂျင်နီယာ ဘာသာရပ်နှင့် အီလက်ထရိုမက္ကင်းနစ်ဘာသာရပ်တို့တွင် အများအားဖြင့် အသုံးချသည်။ ကမ္ဘာမြေတွင်လည်း ကမ္ဘာ့သံလိုက်စက်ကွင်းရှိပြီး ယင်းသည် လမ်းပြစနစ်အတွက် အရေးပါကာ နေလေ (solar wind) များ၏အန္တရာယ်မှ ကာကွယ်ပေးသည်။ လျှပ်စစ်စက်ကွင်းများကို လျှပ်စစ်မော်တာများနှင့် လျှပ်စစ်ဂျင်နေရေတာများတွင် အသုံးချသည်။
ကိုးကား
- Jiles၊ David C. (1998)။ Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials (2 ed.)။ CRC။ p. 3။ ISBN 0412798603။
- Feynman၊ Richard Phillips; Leighton၊ Robert B.; Sands၊ Matthew (1964)။ The Feynman Lectures on Physics။ 2။ California Institute of Technology။ pp. 1.7–1.8။ ISBN 0465079989။