လေယာဉ်ပြေးလမ်း
နိုင်ငံတကာမြို့ပြလေကြောင်းပို့ဆောင်ရေးအဖွဲ့၏ အဆိုအရ ပြေးလမ်းဆိုသည်မှာ လေယာဉ်တစ်စင်း တက်ရန်၊ ဆင်းရန် ပြုလုပ်ထားသော ထောင့်မှန်စတုဂံဧရိယာကို ဆိုလိုခြင်းပင်ဖြစ်သည်။ ပြေးလမ်းမှာ ကတ္တရာ သို့မဟုတ် ကွန်ကရိ လူလုပ်လမ်းများ ရှိသကဲ့သို့ သဘာဝပြေးလမ်းများလည်း ရှိသည်။

.jpg.webp)
သမိုင်း
၁၉၁၉ ခုနှစ် ဇန်နဝါရီတွင် ရိုက်ညီနောင်၏ လေယာဉ်တီထွင်မှုနှင့်အတူ စတင်ခဲ့သည်။
အမည်ပေးခြင်း

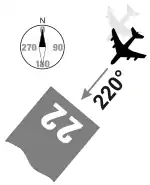
ပြေးလမ်းများကို ပြေးလမ်း၏ လမ်းကြောင်းဒီဂရီကိုလိုက်၍ နံပတ်များဖြင့် အမည်ပေးသည်။ ပြေးလမ်းနံပတ် "09"သည် အရှေ့90°၊ "18"သည် တောင် "180°"၊ "27"သည် အနောက်"270°"၊ "36"သည် မြောက်"360°" ကို ရည်ညွှန်းသည်။ ဥပမာ-ပြေးလမ်း"09"သို့ ဆင်းမည်၊ တက်မည်ဆိုပါက လေယာဉ်ကိုအရှေ့ 90° သို့ ဦးတည်ရမည်။
ပြေးလမ်းကို ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် နှစ်ဖက်လုံးသုံးသည်။ ဥပမာ-ပြေးလမ်း"33"သည် တစ်ဖက်မှကြည့်လျှင် ပြေးလမ်း"15"ဖြစ်သည်။
မျဉ်းပြိုင်ရှိသော ပြေးလမ်းများတွင် အလယ်(C)၊ ဘယ်ဘက်(L)၊ ညာဘက်(R) ဟူ၍ခွဲခြားသည်။ ဥပမာ-ပြေးလမ်း ဘယ်ဘက်၁၅="15L"၊ အလယ်၁၅="15c"၊ ညာဘက်၁၅="15R" ဟူ၍ သုံးသည်။ ပြေးလမ်း "03L"သည် တစ်ဖက်မှကြည့်လျှင် ပြေးလမ်း "21R" ဖြစ်သည်။
မျဉ်းပြိုင်ပြေးလမ်း လေးခုနှင့်အထက်ရှိ လေဆိပ်ကြီးများတွင် ရှုပ်ထွေးမှုများကို ရှောင်ရှားရန် 10°စီ တိုးထားကြသည်။ ဥပမာ-လော့စ်အိန်ဂျလိစ်လေဆိပ်တွင် လေယာဉ်ပြေးလမ်း ၄ ခုမှ မျဉ်းပြိုင်လုနီးပါးရှိသော်လည်း "6L"၊ "6R"၊ "7L"၊ "7R" ဟူ၍ ခွဲခြားထားသည်။ ဖော့ဖရွတ်လေဆိပ်တွင် ပြေးလမ်း၅ခုမှာ "17L"၊"17C"၊17R"၊"18L"၊"18R"ဟူ၍အမည်ပေးထားသည်။
လေကြောင်းထိန်းသိမ်းရေးတာဝန်နှင့် လေယာဉ်တို့အကြား ရေဒီယိုသုံးပြီးစကားပြောရာ၌ ရှင်းလင်းစေရန် " runway three six, runway one four"စသည်ဖြင့် ပြောကြသည်။ "၀"နှင့်စသော ပြေးလမ်းများကို " runway zero six" ၊ "runway zero one left"စသည်ဖြင့် ပြောသည်။

အတိုင်းအတာများ
ယေဘူယျလေကြောင်းပို့ဆောင်ရေးအတွက် ပြေးလမ်းအနေအထားမှာ ၂၄၅ မီတာ (၈၀၄ ပေ)နှင့် အကျယ် ၈ မီတာ (၂၆ ပေ)ဖြစ်သည်။ အပြည်ပြည်ဆိုင်ရာ လေဆိပ်အကြီးကြီးများအတွက်မူ ၅၅၀၀ မီတာ (၁၈၀၄၅ ပေ)၊ ၈၀ မီတာ (၂၆၂ ပေ)ဖြစ်သည်။
ထွက်ခွာ၊ ဆင်းသက်အတွက် အသုံးများမှာ အောက်ပါအတိုင်း ဖြစ်သည်။
- TORA[1]
TODATakeoff Distance Available – The length of the takeoff run available plus the length of the clearway, if clearway is provided.(The clearway length allowed must lie within the aerodrome or airport boundary. According to the Federal Aviation Regulations and Joint Aviation Requirements (JAR) TODA is the lesser of TORA plus clearway or 1.5 times TORA).ASDAAccelerate-Stop Distance Available – The length of the takeoff run available plus the length of the stopway, if stopway is provided.LDALanding Distance Available – The length of runway that is declared available and suitable for the ground run of an airplane landing.EMDAEmergency Distance Available – LDA (or TORA) plus a stopway.
- .[2]
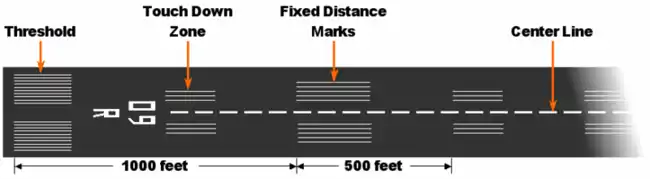
ပြေးလမ်းအမှတ်အသားများ
ပြေးလမ်းများတွင် ပြေးလမ်းအမှတ်အသားများ ရေးဆွဲထားသည်။
ပြေးလမ်းမီးဆင်ခြင်း

ပထမဆုံးပြေးလမ်းမီးကို ၁၉၃၀ တွင် အသုံးပြုခဲ့သည်။
နည်းပညာပိုင်းဆိုင်ရာ


ပြေးလမ်းမီးများကို ညဘက်လေယာဉ်ဆင်းရာတွင် မြင်သာရန် တပ်ဆင်ထားသည်။
- Runway end identifier lights (REIL) – unidirectional (facing approach direction) or omnidirectional pair of synchronized flashing lights installed at the runway threshold, one on each side.
- Runway end lights – a pair of four lights on each side of the runway on precision instrument runways, these lights extend along the full width of the runway. These lights show green when viewed by approaching aircraft and red when seen from the runway.
- Runway edge lights – white elevated lights that run the length of the runway on either side. On precision instrument runways, the edge-lighting becomes amber in the last ၂,၀၀၀ ပေ (၆၁၀ မီတာ) of the runway, or last third of the runway, whichever is less. Taxiways are differentiated by being bordered by blue lights, or by having green centre lights, depending on the width of the taxiway, and the complexity of the taxi pattern.
- Runway centerline lighting system (RCLS) – lights embedded into the surface of the runway at ၅၀ ပေ (၁၅ မီတာ) intervals along the runway centerline on some precision instrument runways. White except the last ၉၀၀ မီတာ (၃,၀၀၀ ပေ): alternate white and red for next ၆၀၀ မီတာ (၁,၉၆၉ ပေ) and red for last ၃၀၀ မီတာ (၉၈၄ ပေ).
- Touchdown zone lights (TDZL) – rows of white light bars (with three in each row) at ၃၀ or ၆၀ မီတာ (၉၈ or ၁၉၇ ပေ) intervals on either side of the centerline for ၉၀၀ မီတာ (၃,၀၀၀ ပေ).
- Taxiway centerline lead-off lights – installed along lead-off markings, alternate green and yellow lights embedded into the runway pavement. It starts with green light at about the runway centerline to the position of first centerline light beyond the Hold-Short markings on the taxiway.
- Taxiway centerline lead-on lights – installed the same way as taxiway centerline lead-off Lights, but directing airplane traffic in the opposite direction.
- Land and hold short lights – a row of white pulsating lights installed across the runway to indicate hold short position on some runways that are facilitating land and hold short operations (LAHSO).
- Approach lighting system (ALS) – a lighting system installed on the approach end of an airport runway and consists of a series of lightbars, strobe lights, or a combination of the two that extends outward from the runway end.
ထိန်းချုပ်ခြင်း
ပုံမှန်အားဖြင့် မီးများကို အေတီစီ တာဝါမှ ထိန်းချုပ်သည်။
ကိုးကား
- Order JO 7340.1Z: Contractions (PDF)။ Federal Aviation Administration (March 15, 2007)။
- Airplanes: Turbine engine powered: Takeoff limitations၊ 2009-10-04 တွင် ပြန်စစ်ပြီး
- FAA AC 150/5340-1L – Standards for Airport Markings pages 13 and following

